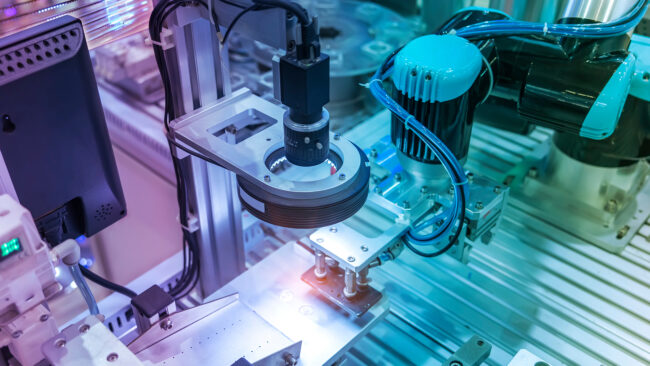
In today’s rapidly evolving manufacturing landscape, staying competitive and efficient is paramount. Manufacturers are constantly seeking innovative solutions to streamline production processes, reduce defects, and ensure product quality. One such groundbreaking solution is vision integration, a technology that empowers machines to “see” and make informed decisions based on visual data.
Understanding Vision Integration
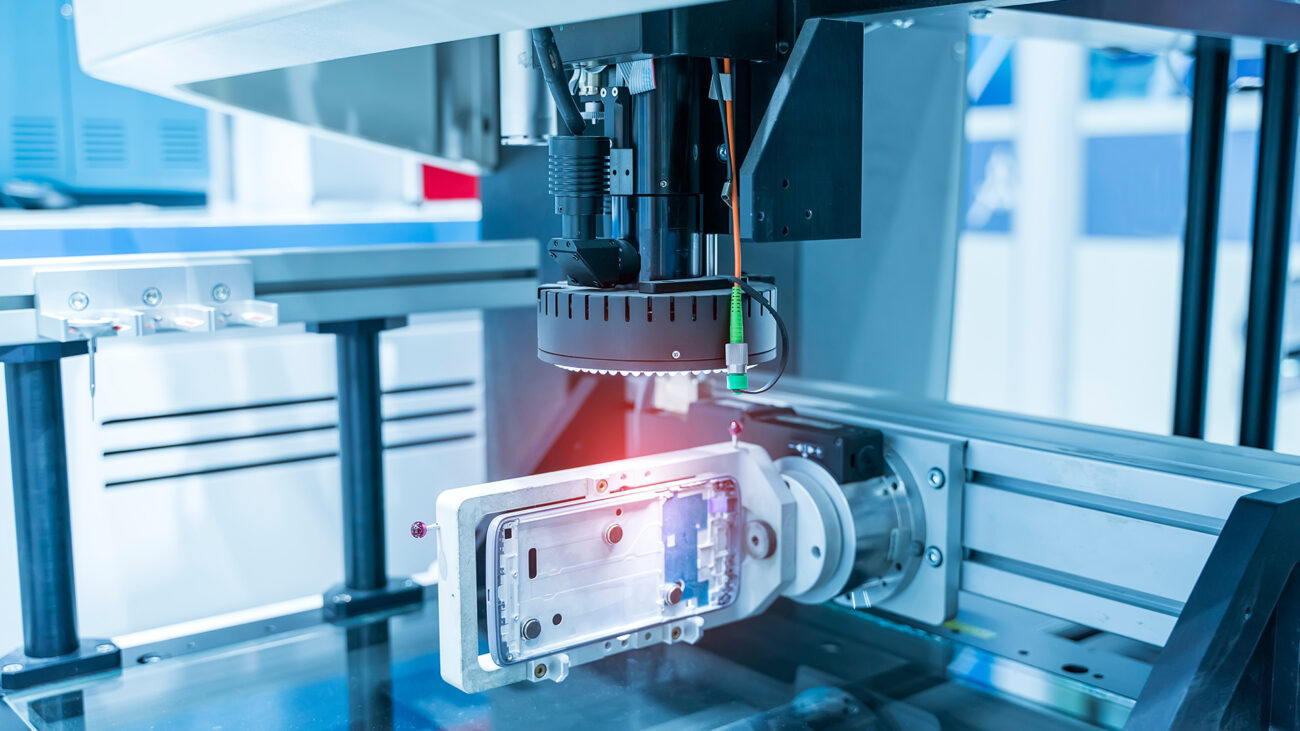
Vision integration is the process of incorporating vision systems, typically consisting of cameras and image processing software, into manufacturing processes. These systems enable machines to capture, analyze, and interpret visual information, much like the human eye but with incredible speed and precision. The key to their effectiveness lies in their ability to make split-second decisions based on this data.
Applications in Manufacturing
Vision integration has found a myriad of applications within the manufacturing sector, transforming various aspects of the production cycle. Here are some notable examples:
- Quality Control: One of the most critical applications of vision integration in manufacturing is quality control. Cameras and image analysis software can identify even the tiniest defects, ensuring that products meet the highest quality standards. For instance, in electronics manufacturing, vision systems can spot minuscule soldering flaws that might escape the human eye.
- Assembly Verification: Ensuring that components are correctly assembled is paramount to product functionality and safety. Vision systems can validate that parts are properly aligned and assembled, reducing the risk of errors and costly rework.
- Robot Guidance: Manufacturing robots are becoming increasingly sophisticated, thanks to vision integration. These systems allow robots to “see” their surroundings and make real-time adjustments, such as picking and placing objects accurately, even when they vary in size, shape, or orientation.
- Measurement and Gauging: Precise measurements are critical in manufacturing. Vision systems can accurately measure dimensions, angles, and other attributes of products, providing invaluable data for quality assurance and process optimization.
- Barcode and Text Reading: Manufacturing relies on precise identification and tracking. Vision systems excel at reading barcodes, QR codes, and text, ensuring that products are correctly labeled and can be tracked throughout the supply chain.
- Packaging and Labeling: Vision integration can also verify that products are correctly packaged and labeled, reducing the likelihood of packaging errors and improving overall efficiency.
- Defect Detection: In industries where defects can have far-reaching consequences, such as aerospace and automotive, vision systems excel at defect detection, contributing to the production of safer and more reliable products.
The Vision Integration Process
Implementing vision integration in manufacturing involves several crucial steps:
System Design: Select the appropriate cameras and image processing software for your specific application.
Software Development: Develop or configure the necessary image processing algorithms to extract meaningful information from the visual data.
Calibration: Ensure the cameras and vision systems are calibrated to provide accurate measurements and perception.
Integration: Integrate the vision system with your manufacturing process or control systems to make real-time decisions based on visual data.
Testing and Optimization: Thoroughly test the integrated system and optimize algorithms and settings for optimal performance.
Maintenance and Support: Provide ongoing maintenance, updates, and support for the integrated vision system to ensure it continues to deliver value.
Use Vision To Improve Your Manufacturing Process
In the ever-competitive world of manufacturing, vision integration is a game-changer. By harnessing the power of cameras and image processing, manufacturers can boost efficiency, reduce defects, and maintain the highest quality standards. From quality control and assembly verification to robot guidance and defect detection, the applications are limitless. Embracing vision integration is not just about automation; it’s about achieving new levels of precision and ensuring a competitive edge in the global market. As technology continues to advance, we can only expect vision integration to play an even more pivotal role in shaping the future of manufacturing.